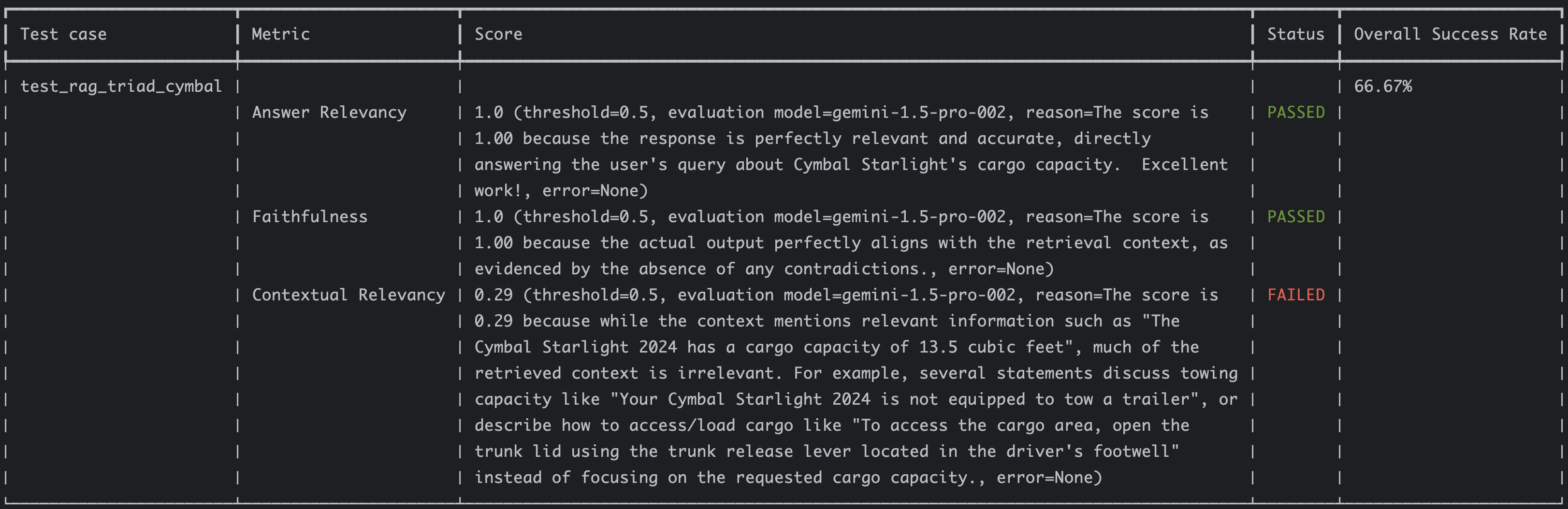
Previously, I showed how to do RAG with a PDF using LangChain and Annoy Vector Store and RAG with a PDF using LangChain and Firestore Vector Store. Both used a PDF as the RAG backend and used LangChain as the LLM framework to orchestrate RAG ingestion and retrieval.
LlamaIndex is another popular LLM framework. I wondered how to set up the same PDF based RAG pipeline with LlamaIndex and Vertex AI but I didn’t find a good sample. I put together a sample and in this short post, I show how to set up the same PDF based RAG pipeline with LlamaIndex.
Read More →