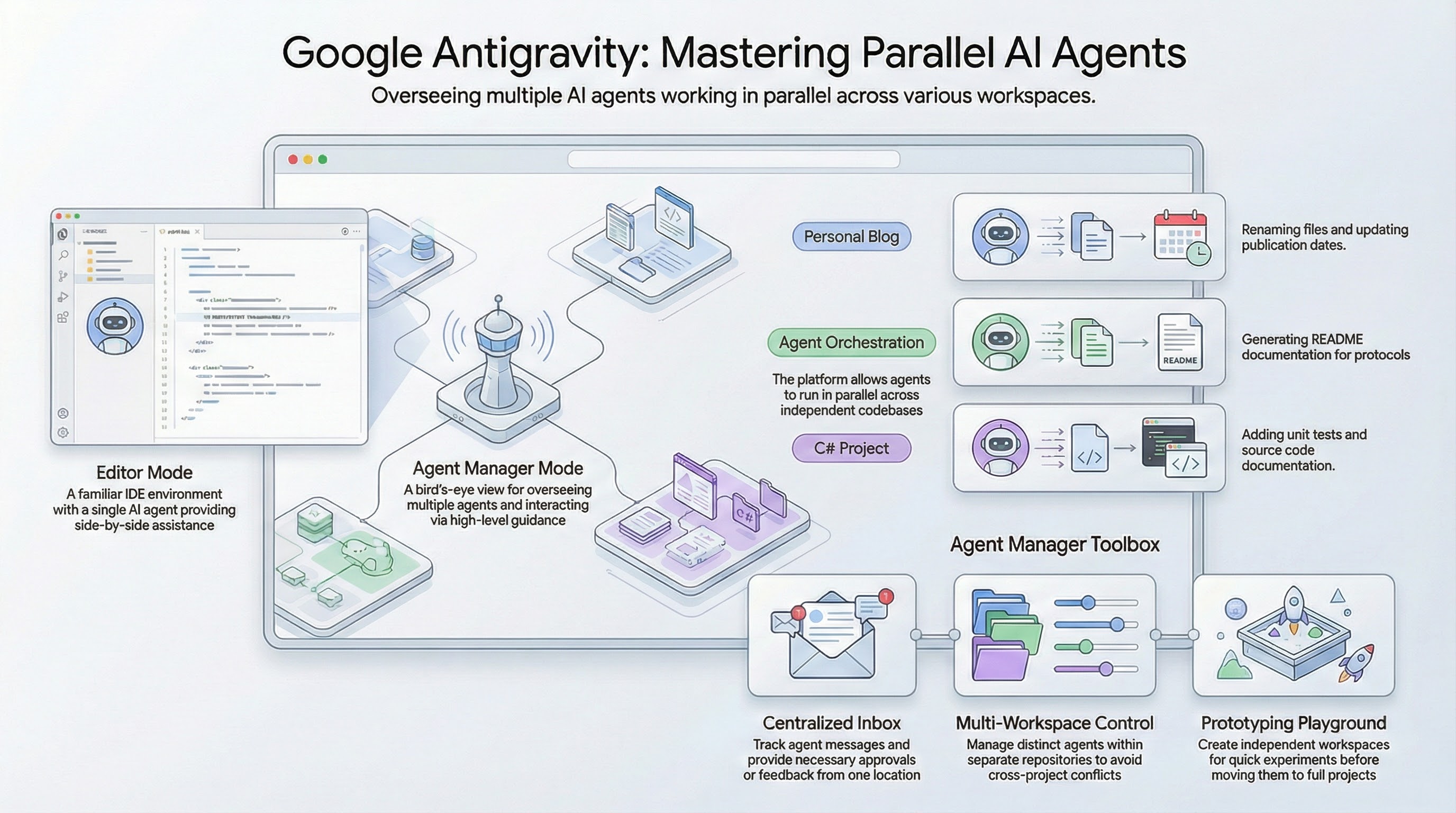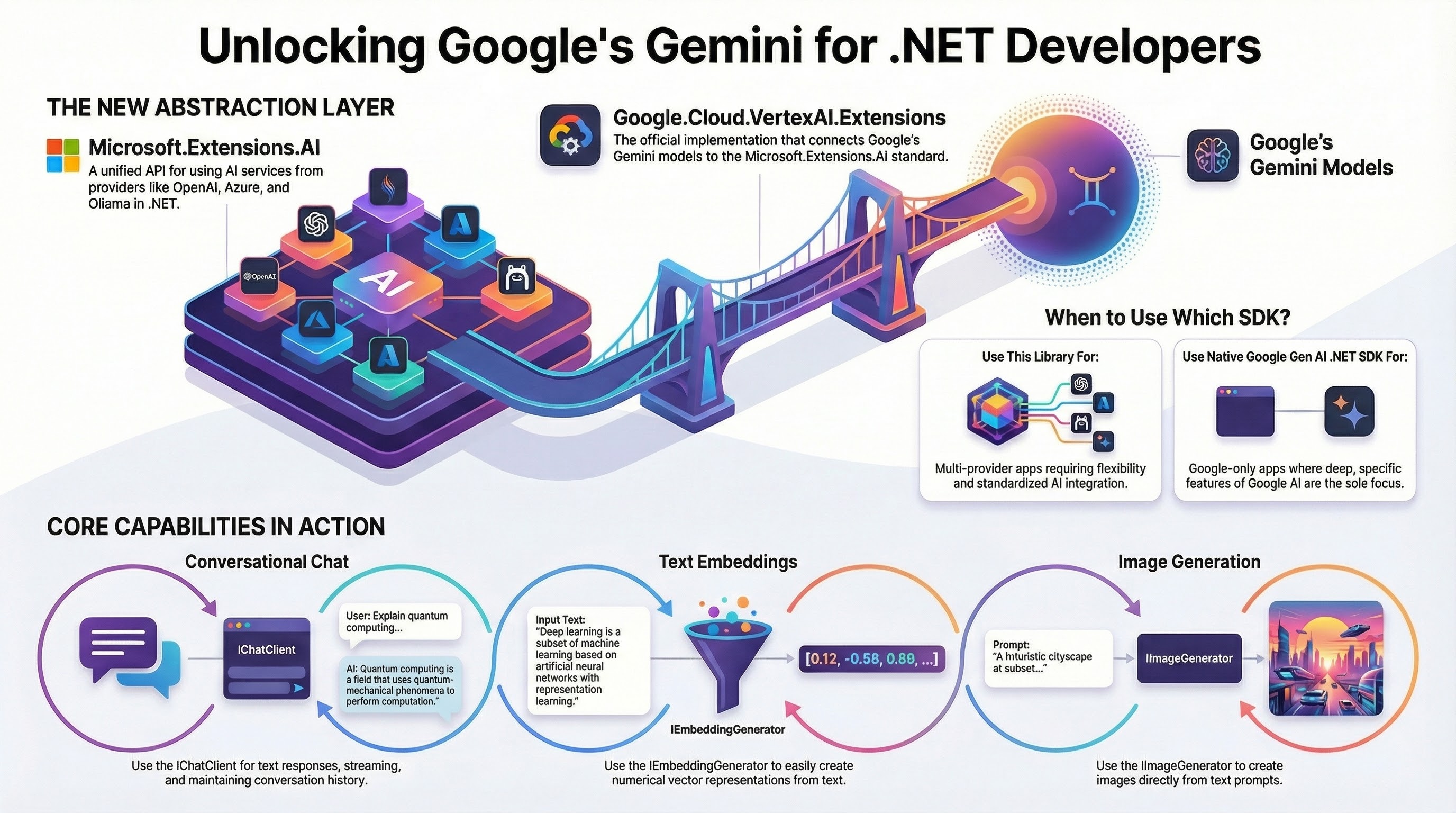
In October 2024, Microsoft announced the Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Abstractions and Microsoft.Extensions.AI libraries for .NET. These libraries provide the .NET ecosystem with essential abstractions for integrating AI services into .NET applications from various providers such as Open AI, Azure, Google.
Today, we’re happy to announce the Google.Cloud.VertexAI.Extensions library. This is the Vertex AI implementation of Microsoft.Extensions.AI. It enables .NET developers to integrate Google Gemini models on Vertex AI via the Microsoft.Extensions.AI abstractions.
Let’s take a look at the details.
Read More →